Fanless PC
How Heat Impacts Your Computer, and Should You Be Concerned?
Jarltech's fanless embedded computers represent the cutting edge of embedded computing technology, offering an ideal solution for remote monitoring and control applications.
Our product range includes a variety of modular I/O solutions that are readily available, allowing customers to rapidly deploy a range of applications and fully leverage the benefits they offer.
Which Components Produce Heat?
It is important to note that the core components of a computer, including the Central Processing Unit (CPU) and the Graphics Processing Unit (GPU), generate heat during operation. The CPU, which is responsible for executing algorithms, and the GPU, which handles 3D imaging, both contribute to heat production. It is not uncommon for gaming to result in elevated temperatures, as GPUs are responsible for handling complex calculations, which can generate more heat than CPUs. Furthermore, hard disk drives can contribute to heat generation, particularly when handling large file transfers.
What effect does heat have on your hard drive?
While hard drives do not consume as much power as the CPU or GPU, they are highly sensitive to temperature fluctuations. It is important to note that excessive heat can cause severe damage to your hard drive. Heat can cause components to expand, potentially leading to warping and improper disc reading. While this may be an extreme example, it highlights the necessity of replacing the HDD in the event of such damage.
It is important to note that heat can significantly impact the lifespan of your hard drive. As stated by National Instruments, a temperature increase of just 5°C above ambient can reduce a drive's expected lifespan by up to two years. Nevertheless, the relationship between elevated temperatures and drive failure rates remains a topic of contention. Google engineers have determined that, within moderate temperature ranges, other factors may have a greater impact on failure rates than temperature alone. Hard drives that are more than three years old are more prone to heat-related complications. While data recovery is typically feasible, addressing a damaged hard drive can be intricate.
How does a fanless PC maintain optimal operating temperatures?
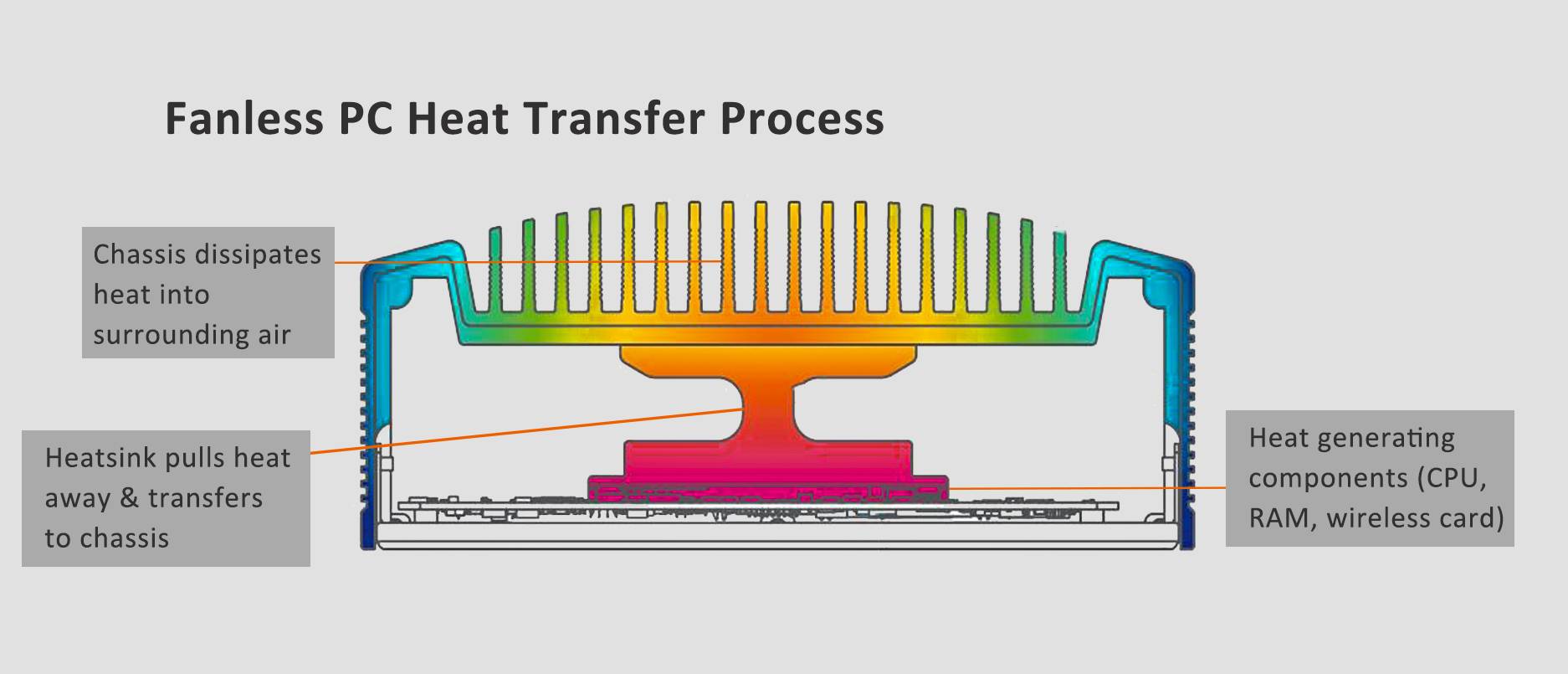
While a fanless PC may not look significantly different from a traditional PC, especially compact models with fans, it uses subtle yet effective methods to manage heat. Fanless systems primarily rely on conduction to dissipate heat, transferring it from hot components to their surroundings through direct contact. Although heat conduction is a natural process, its efficiency can be greatly improved through thoughtful design.
The fundamental concept entails linking heat-producing components, such as the CPU, to a heat sink. The heat sink is designed to absorb and transfer the heat generated by these components into the surrounding air. The effective design of a heat sink assembly requires the careful selection of materials and a thorough analysis of how its various parts will interact to optimize heat dissipation.
To ensure effective heat transfer, a variety of strategies are employed both inside and outside the PC
It is of the utmost importance to minimize air gaps between the CPU and the heat sink within the PC, given that air is a poor conductor of heat. Despite the use of a heat sink mounted directly on the CPU, the presence of surface imperfections may result in the formation of microscopic air pockets. To address this issue, thermal paste is applied. The thermal paste, which conducts heat more effectively than air, fills the gaps and ensures a more efficient transfer of heat from the CPU to the heat sink.
When it comes to the exterior of the PC, a distinct approach is required when it comes to heat dissipation into the air. One effective design is a lid with specially engineered ridges that enhance the surface area exposed to the air, thereby improving heat dissipation. The additional pathways created by the ridges allow for more efficient heat dissipation.
To ensure optimal results when working with fanless PCs, it is essential to adhere to the following principles. While thermal paste is an effective heat conductor, it is less effective than materials like copper or aluminum. It is important to use only the necessary amount of thermal paste to fill gaps, as excess paste can create a thermal barrier and lead to overheating. Furthermore, it is advisable to refrain from placing any objects on top of a fanless PC, as even a single sheet of paper can impede the flow of hot air, thereby hindering the cooling process. It is also important to consider the surrounding air quality, as inadequate circulation in confined spaces or thin air at high altitudes can reduce the efficiency of heat dissipation.
The majority of Logic Supply heat sink assemblies comprise two principal components: an aluminum block that is positioned on top of the CPU, and the case lid. Heat is transferred from the CPU to the aluminum block, then through the lid, and eventually into the surrounding air. To guarantee optimal cooling, it is crucial to have effective heat-conducting interfaces between all these components.
How to Design an Efficient Heat-Conducting Interface
Adherence to these principles will assist you in avoiding common issues when assembling or using a fanless PC. While thermal paste conducts heat better than air, it is far less effective than copper or aluminum. Therefore, it is important to apply only enough to fill the necessary gaps. Using an excessive amount can result in the formation of a thermal barrier, which may lead to overheating. It is also inadvisable to place objects on top of the fanless PC, as even a small item such as a sheet of paper can impede the flow of air and hinder the cooling process.
Even a single sheet of paper placed on the PC's lid can impede proper cooling by trapping heat. It is also important to consider the surrounding air. If it cannot circulate freely, for example in a confined space, or if the air is too thin, as at high altitudes, it will be less effective at dissipating heat from the PC.